THE AMERICAN KERRY AND DEXTER CATTLE CLUB BULLETIN FOUR
From Judy Sponaugle








THE AMERICAN KERRY AND DEXTER CATTLE CLUB BULLETIN FOUR Read More »
HistoricalFrom Judy Sponaugle








THE AMERICAN KERRY AND DEXTER CATTLE CLUB BULLETIN FOUR Read More »
Historical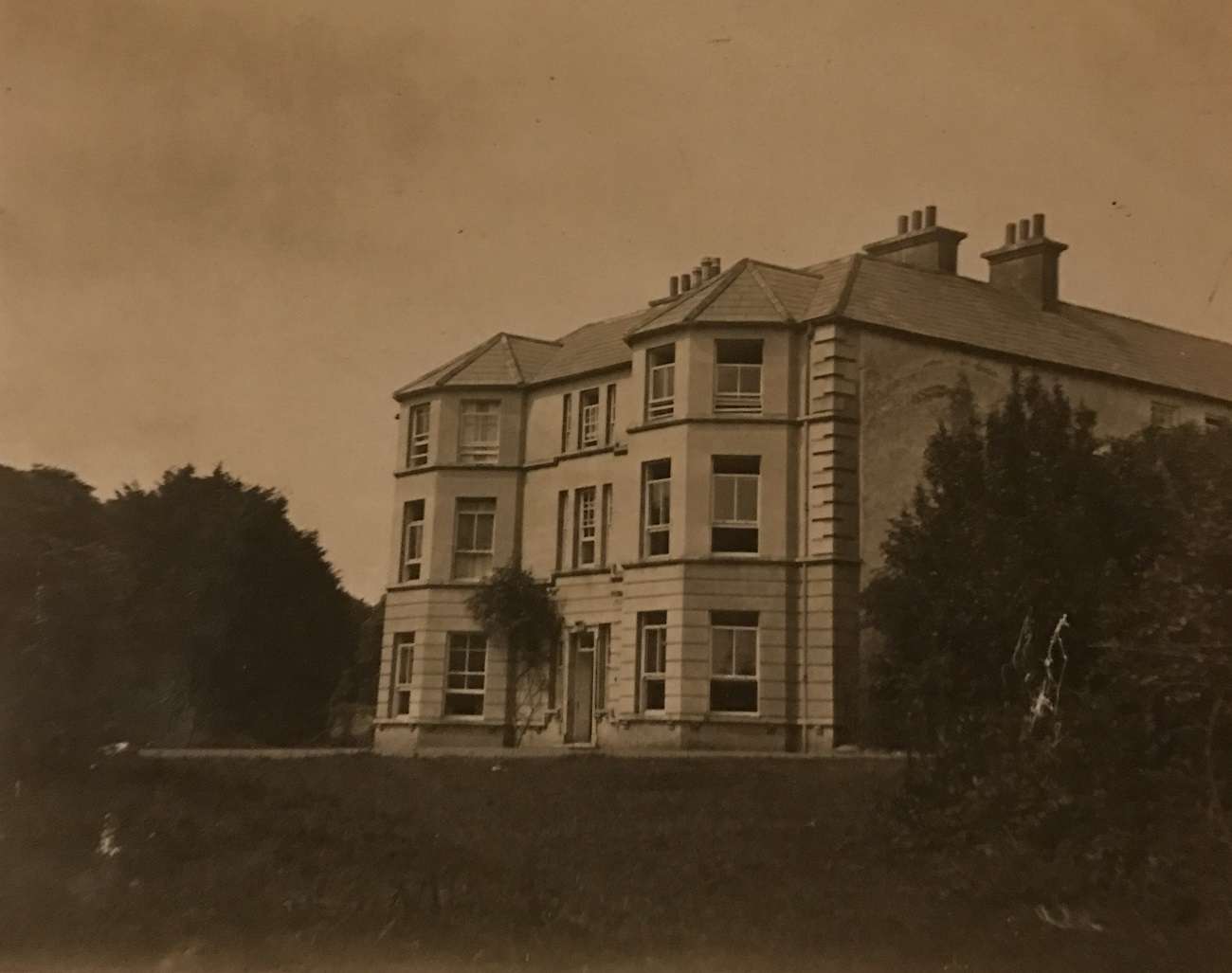
I usually like to start these articles with a picture of a Dexter cow from the past, that will be the focus for the historical adventure, as we travel back in time. But sadly, this time I have no beautiful and memorable cow to set the tone, as one could not be found for a lasting memory. Instead, I will show you a photo of Chute Hall. Chute house was thought to be built in the eighteenth century. In 1906 Chute Hall was documented to be owned by Rowland Chute. Rowland E. Chute owned it along with an additional house by the name of Leebrook House on the same estate. It remained in the family until 1930. Chute Hall was demolished in 1957 and no longer remains, but the memory of Leebrook House lives on in the Ballygarry House Hotel that has come to replace it. You could travel there for a nice stay in the beautiful hotel. Why is Leebrook significant? It was the herd name associated with Rowland E. Chute, who was a landed gentry in country Kerry. He was actually a judge for the Royal Dublin Society allowing Dexters to be entered into the herd books. The lack of history on his herd and the small bit of information that can be found is reveling to why the name of the Leebrook herd never took off.

I speak a lot on the hardiness of the Dexter breed. Reminding people that they have been historically known to get by on less, endure hardship and stay productive where other cattle may not. As this above article states “They are hardy, wiry, vigorous in constitution, and capable of making a living where bigger cattle would starve. Some of their pastures are so poor that it is marvelous how they manage to pick their substance at all, but they come home sleek and satisfied for all that.” But, as responsible cattle breeders we must also balance this knowledge with the full responsibility that we must care for the nutritional needs of our animals. So that no new cattle owner may exploit the hardiness of the Dexter to such extremes of nutritionally depriving their hardy livestock, I wrote this article as a historical reminder of where this can go. Dexters in Ireland were naturally small for many reasons, some described as no bigger than a Newfoundland dog. Some of this is genetics while some may actually be due to a lack of proper nutrition in extreme situations. In England on the fertile land where they were pampered by English Aristocrats it was a known fact that the Dexters grew larger and fattened better. Some of this to the benefit of the Dexter, while some may have been a bit more pampered than they may really have needed. Balance over all is good for animals, providing adequate nutrition to be productive while letting them work for their food by grazing and giving them a proper environment to do so. A balance fosters good health while retaining their hardy genetics so that they may best serve their owners with reliable productivity.

Here we will see the significance of Rowland Chute in my historical wanderings of Dexter cattle. Rowland Chute sent a photograph of a prize-winning bull (I wish had that photograph) to a prospective buyer, Mr. Spencer to help persuade him into buying his cattle. I tried to research and find information on what bull this could have been but turned up no results when looking for a Leebrook (Chute’s herd name) bull, so I must assume that the bull was of a different registered herd name. It sounds as though Chute may have sent a picture of a prize-winning bull and the buyer may have purchased stock thinking they would resemble the bull in the photograph. What the buyer received was in no wise up to his expectations but rather “not much bigger than a Newfoundland dog, and the other cattle were in an emaciated condition”. Chute’s response was “that the cattle were always in low condition because they lived hardily on the hills”.

Chute claimed his Dexters were in “normal condition” because the cattle were “always in low condition, because they lived hardily on the hills”. Chute was surprised to hear the animals were emaciated and unhealthy but then admitted that he sent a description of cattle that were not actually in his possession. Instead, he sent a photograph of a prize bull! It does cause the mind to wonder where these animals may have been obtained from, just wondering the hills waiting to be snatched at the moment a perspective buyer was found. Witnesses definitely backed up the claim of the poor condition of the Dexters. Most importantly a veterinarian said that they were in disgraceful condition. Those are strong words; he did not just say they were in low condition but disgraceful! The bull was not much bigger than a Newfoundland dog. A male Newfoundland dog may weigh as much as 150 pounds and stand at 28inches tall. To consider the size of a Newfoundland dog see the story here where a Newfoundland Dog and a little Shetland Pony similar in size “have struck up an unlikely friendship”. https://www.chroniclelive.co.uk/news/north-east-news/newfoundland-dog-forms-unlikely-friendship-21682333

In this article Rowland Chute, the plaintiff was requesting £53 to recover the cost of the Kerry Dexters sold to Mr. Spencer Whatley. Mr. Watley countered that Chute should pay 62 £ for the keep of the unfit cattle upon their arrival since they were delivered. The County Court, Lambeth delivered in favor to Chute awarding him his claim of £53 and dismissing the counter claim from Mr. Watley. Mr. Rowland Chute was vindicated that day of his charges, but a further look into the Herd books shows that Rowland Chute had a very limited future with Dexters. When I searched for records, I found only 3 registered cows with the prefix Leebrook. Leebrook Cush, Leebrook Darkie and Leebrook Stella. All of these three cows were owned and bred by Rowland E. Chute and Qualified by inspection. If I were to guess they were possibly inspected by Mr. Chute himself since he was a judge for the Royal Dublin Society. None of these cows show any offspring that I can find. One cow’s date of birth is listed as 1898, the other listed as Dec 11, 1898 and the last Dec 20 1898. I later found Chute appointed an officer for the “Kerry and Dexter Cattle Society of Ireland” in 1917 written in the Kerry Evening Post. For a man who was so involved with Dexters, appointed a judge and an officer, he has a very small number of Dexters registered to his name and you can’t but wonder if his cattle that were once said to be “in a disgraceful condition” had something to do with why. If a breeder wants to stay long in breeding any form of life one must attend to its needs and we must never give hardiness as an excuse for a true form of neglect. I will not develop any conclusive opinion on Mr. Chute as there were some incredibly small Dexters in Ireland, as I said before partially due to genetics and diet. Chute was said to have had a bull that weighed 8 stones and a quarter (115.5 pounds). The 3-year-old bull measuring at 30 inches from hoof to tip of shoulder was said to be in high condition. The comment was made in reference to this bull, “Yet a more perfect specimen of superior symmetry was not perhaps to be met with throughout the show.” This bull I will wager was the prize bull that was previously mentioned. It is fair to say that most Dexter owners will want a Dexter to fatten out at a larger weight than 115 pounds, live weight and if properly taken care of you may nearly guarantee today, whatever type of Dexter you raise, they will by 3 years old.


My full intent in researching this information was to be thorough, but I also know that the history of Dexter cattle is extensive and recognize that even with every good effort I could possibly be missing information in my research to enlighten us on the situation of Rowland Chute. I will take no hard line in conclusion on the matter of Mr. Chute but rather leave it in the hands of the reader.
-Danielle of Bryn Mawr
Information may not be reproduced without giving credit to the author.
Dexters No Bigger Than Dogs Read More »
HistoricalIf you looking for more information on our wonderful breed, scroll down past the digital magazines to the flipboard section. There are several of the Dexter Registry Magazines that have been converted into easy to view flipboards. So much history at your fingertips in one place, the IDC Gazette.

Here is what a Dexter family gathering looked like in the 1800s. Notice that the cottage cow is handled pretty much like the family horse. This photo was taken from the Facebook group DexterCattle Historical with the permission of Judy Spongaule. Judy has a wealth knowledge about our wonderful breed.
What a Dexter family gathering! Read More »
Historical



Dexter Cattle put a high emphasis on dairy traits and beef traits equally. Thoughtful breeders were honing these Irish cattle to excel in both capacities. One of the ways they were doing this, was by selecting bulls from dams with known milk records. Pedigree information is interesting to reflect on when you see repeated names in pedigrees and photos to document what genes might have been passed on from their ancestors. Looking at a bull alone will never tell you anything deeper about his genetics, than what you can evaluate with your eye. A nice-looking bull tells you nothing about what type of milk production his dam might of possessed. Thankfully with photos we can look back on bulls like Atlantic Spratt and see that he had a lot to offer besides just good looks. The fact that Spratt was presented at the show tells us that his dam was qualified by performance records, because it was a requirement to enter the show. Though none of the cows are perfect and much improvements can still be had in generations to come, evaluating them and their records goes to show that they were cows that could surely fill the pail.
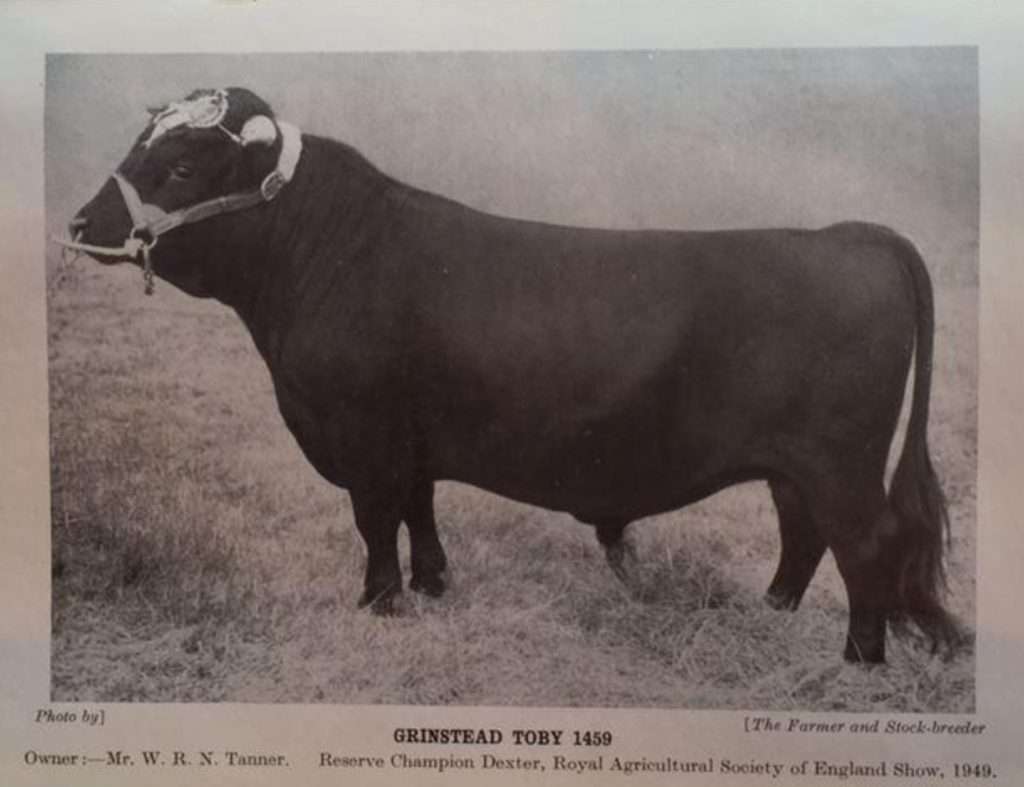

From this photo we can see where Atlantic Spratt got some of his good looks from. His sire was Grinstead Toby, a Reserve Champion Dexter, but to dig deeper I will investigate some of the females in Toby’s pedigree.
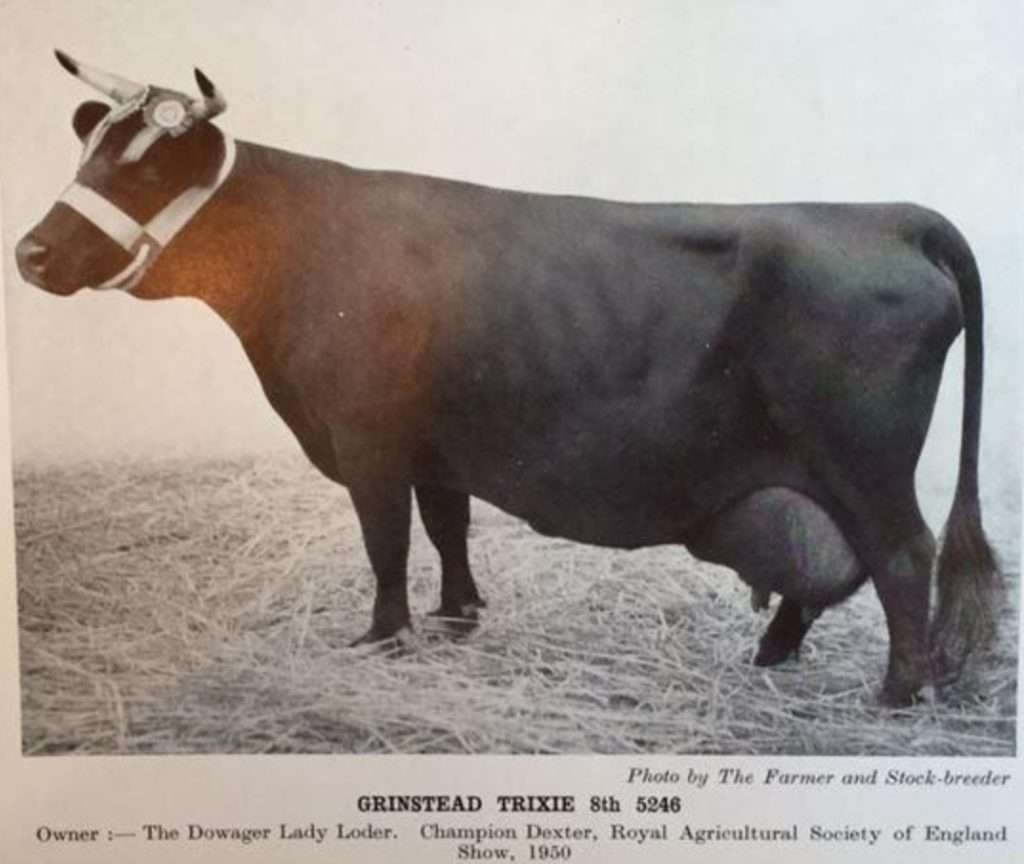


This is Grinstead Trixie the 8th. Lady Loder the breeder, was known for only selecting sires out of cows with proven milking records. Though this cow may seem like she has less than perfect attachment at 10 years old(the age in photo), she looks to have a good amount of volume. You will see in the article above, Trixie is “Queen of the Dairy Show” in October 1953 (then 13 years old and winning first prize for 3 running years). She was a top Dexter cow out of cows that were milking at 4 and a half gallons of milk a day. Lady Loder was known to cull hard and keep to a high standard. Trixie the 8th could have had improved udder attachment, but she definitely filled her part as a solid milk cow. Now I shall dig a bit further back in history to give the reader a greater understanding. Let us next consider Grinstead Trixie the second and likewise the original Trixie herself.
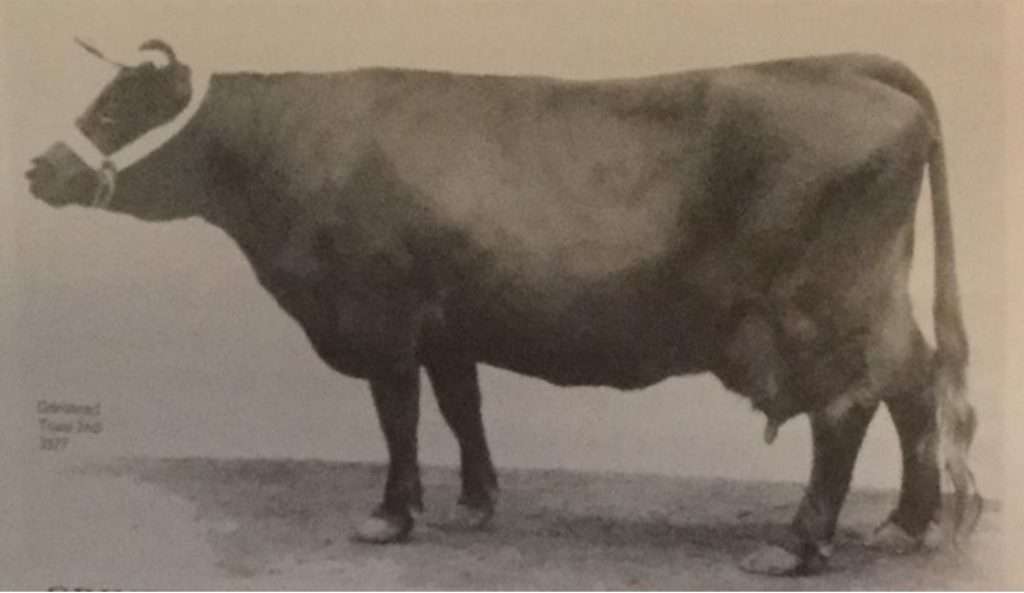

Just to give a very interesting historical compass to the full impact of the Grinstead Trixie line, let us delve deep into history, back to November 1919 when the original Trixie was being written about. The original Trixie was one of an original 12 cows that were obtained by Lady Lodger. Of those original cows she only kept three, Trixie being one of three top cows. Those 3 cows were chosen for their milking powers. Trixie was born in 1904 and was a foundation cow for the Royal Dublin Society. By 1919 she had produced her 14th calf, proving to be productive and already fairly long lived. What an exceptional cow to start your herd from. This cow was the foundation of Lady Loders Grinstead herd and imprinted her name on the herd for generations to come. Lady Loder in other statements had complained about some of the low quality Dexters that were being sold. Lady Loder may not have started with the best stock, but she culled down to just three cows to build her herd from and only used proven bulls that possessed dairy traits worth passing on to their offspring. She had a focused eye that considered the breed standard when evaluating and considering her Dexters by. Her legacy is one worth being remembered and replicated, showing you do not need much to start out with, but rather have a quest for quality and be willing to cull to obtain it.
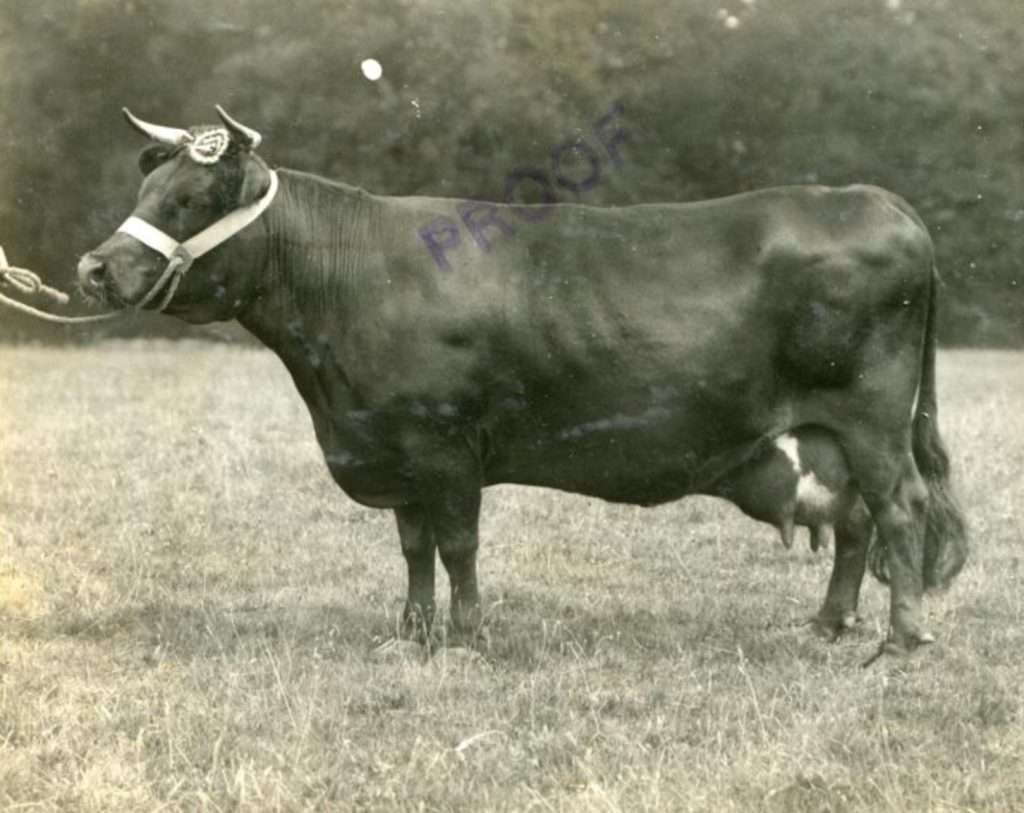


Murrel Peach Blossom who was likewise related to Atlantic Spratt was a challenge cup winner.
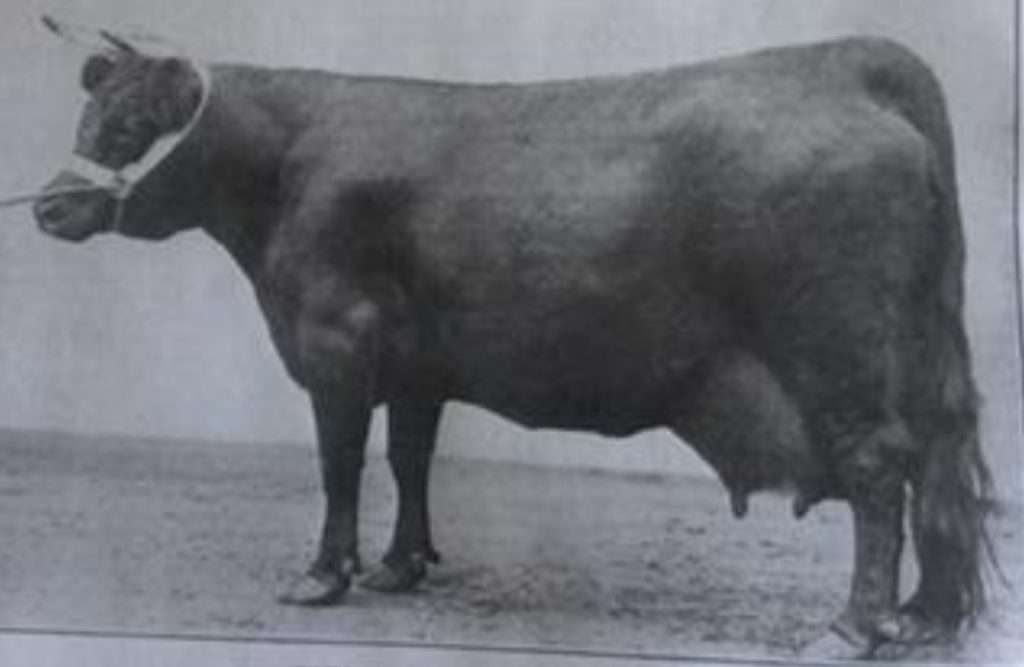

Grinstead Hawk obtained a register of merit for milk production in 1940, won 1st in the milking trails and won the reserve Nutt challenge cup and many more competitions. Though her flat feet and titlted teat may jump out as not quite perfect, there is much to be appriciated in a cow with solid milk production.
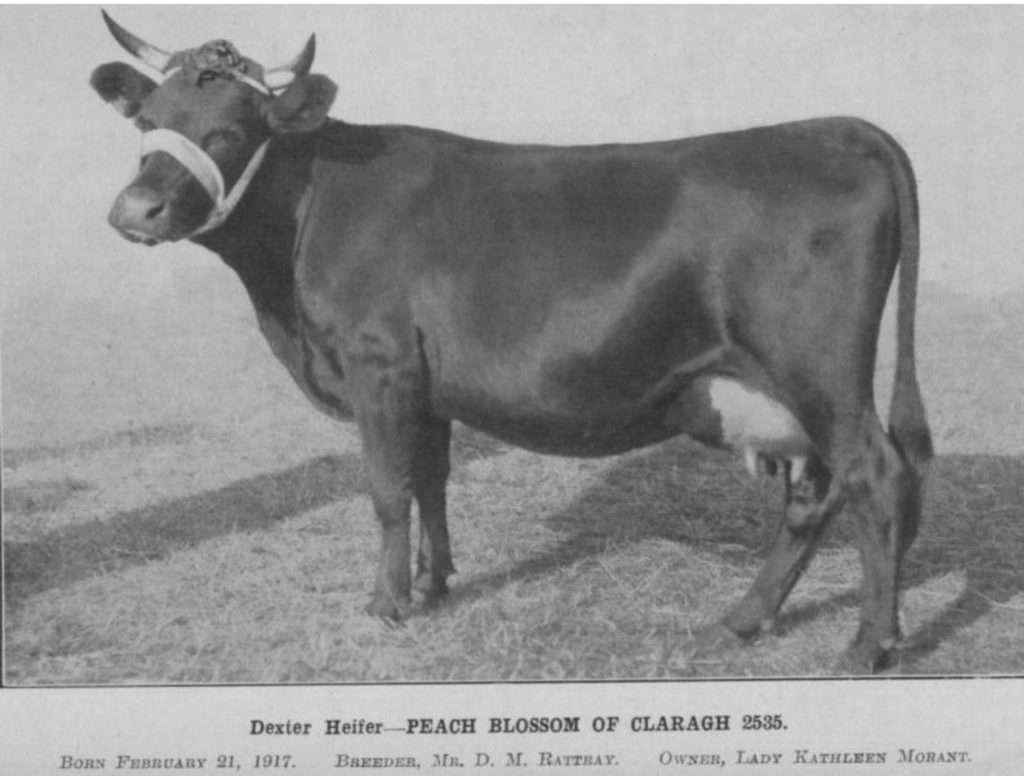

Peach Blossom of Claragh won 2nd place for a cow in milk while competing against mature cows.
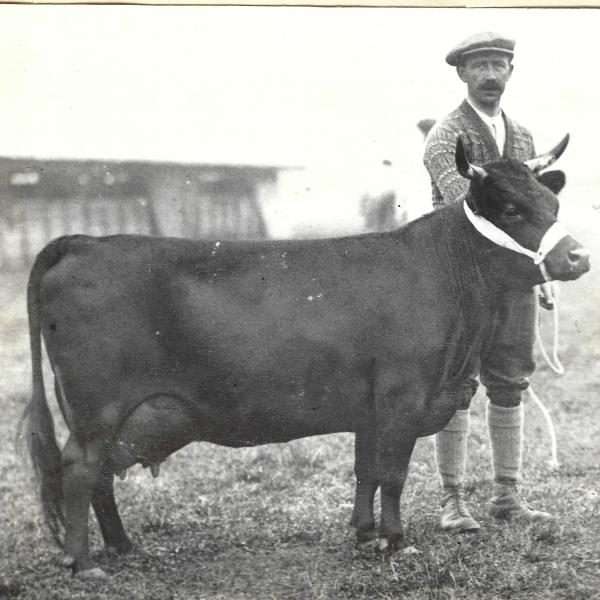

In conclusion to this article, I will leave you with this cow Grinstead Watercress, bred by Lady Loder though not directedly related to Spratt. This cow is graceful and well balanced a testament to her breeding. Some may say that she is not deep enough, but for a cow that I believe to be non chondro born in 1920 I’d say she is quite beautiful indeed. I hope this article inspires people, no matter the size of your herd or no matter how long you have been breeding that their is always room for improvement, no matter the current genetics in your herd. In order to truely preserve the wonderful Dexter traits of yesterday we must also be willing to impove our cattle of today.
“Dairy Breed” Champion Dexter Bull Atlantic Spratt Read More »
Historical
The old saying “No feet, no cow” is a phrase that denotes the importance of a cow’s ability to walk. Without good feet there can be no cow to stand on them, thus causing peril to the health of the cow. No Udder, no cow could be a similar maximum, denoting the importance of the cow’s udder. Without a good functioning udder, a cow cannot fulfill her role to nourish a calf or humans thus degrading her value as a cow. Not every Dexter needs an udder like Atlantic Alison, but the quality of a Dexter cow is tied up in the function and quality of her udder.
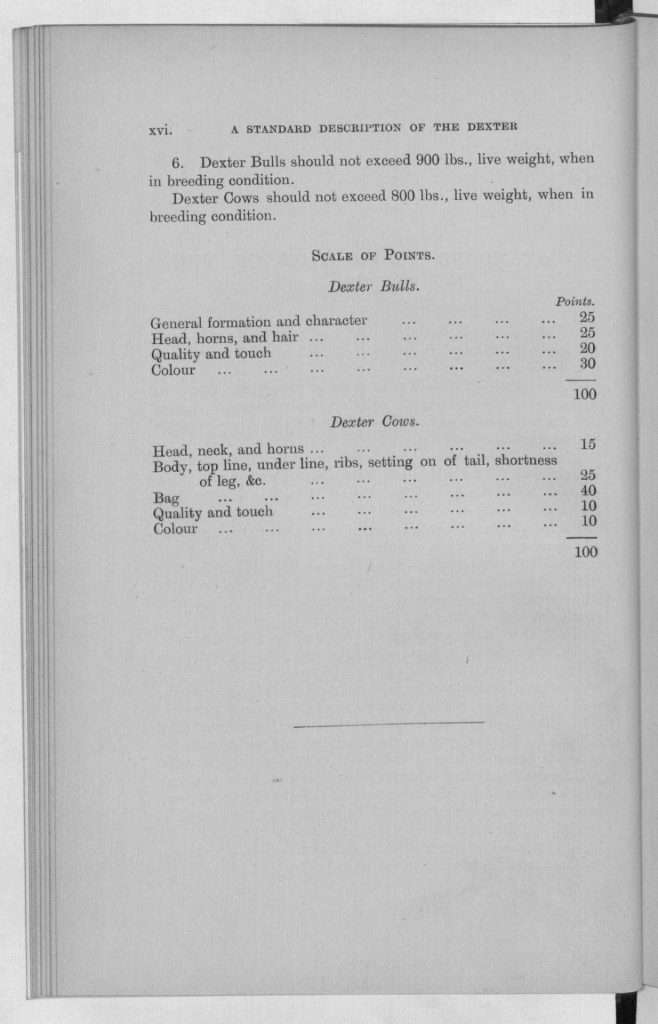
This scale of points as seen above, is the first scale of points written for Dexter cattle and the most authoritative in breed history. It makes it clear what values can be attributed to a Dexter cow. As you can see udder traits are very important to the Dexter breed. There is no room in the Dexter breed for cows with truly bad udders, as it’s not agreeable to the standard scale of points. So, you see, 40% of a Dexter cows value of points is wrapped up in the quality of her udder, where only 25% goes for her body. That 25% is not just shortness or depth alone but “body, top line, under line, ribs, setting of tail, shortness of leg &c.” The point is cows with good udders are very important to the breed. A cow that lacks valuable udder points would scale very low as a Dexter in general. A cow that is not perfectly short could still score quite high as a Dexter if all other traits were ideal. A short Dexter with a bad udder would easily be beat by a taller Dexter with good conformation and an excellent udder.
Many may not know that the Dexter at one time was known to have milking properties of equal merit as the Kerry, a known dairy breed, though they are a dual-purpose breed. Mr. R Tait Robertson was to of said ” The milking properties of both breeds may be said to be of about equal merit”. Who is R. Tait Robertson? He is the son of James Robertson, of whom bred or collected a large portion of the foundation Dexters sold to England and other places. He was an influential breeder. For an interesting photo reference of the amazing similarities of Dexter and Kerry cattle see Aicme Check (Dexter cow) and Greenah Florah 2nd (Kerry cow). I did not have to hunt far and wide to find examples that looked closely related. All I had to do is go to the 1901 Herd book and find the only available photos of an example Kerry and Dexter cow. And by the way note the classic white Dexter udder marking on the Kerry cow as this was a common Kerry trait feature too. Nose to nose as you can see in the photo comparison they do look quite alike.


Historically looking at the Dexter milk properties! Read More »
HistoricalBorn Survivor – Story of the Dexter – Heritage Cattle.
Dexter Cattle Return to Ireland Read More »
Historical
Dexters are well known as Irish Dexters even if many other points about them are debated. The above bull though registered with the Dexter Cattle Society is an Irish Dexter with a “fine type and constitution” as the article states. I checked, he certainly was owned and breed by Mr. W. Lindsay Everard of Ratcliffe. This article holds true to the fact that Dexters are known to be of a small type of cattle. That very small cattle were known to roam Ireland before “Mr. Dexter” was ever penned in History. In Kerry there was known to be some of the smallest type of cattle one can imagine, long before Dexters were ever established or organized into a true breed. So small of an animal that it is mentioned in this paragraph, but yet still producing 2 gallons of milk a day is a marvel indeed. The brown article was written on 14 Nov 1929, it’s from the Western Daily Press Bristol. The picture was taken from a later newspaper published in 1930. Though the Dexter was well known to produce ample milk and was “closely allied to the Kerry breed and very similar to it in general appearance.” The differences being that “Dexters are “more stoutly built and rounder in their contours”.


The Dexter has a “stronger head than the Kerry, but very clear cut, shorter below the eyes and broader at the muzzle”. The description of her horns are as follows ” Her horns are thicker and usually after rising upwards bend backwards towards the points”. It is interesting to note that she is even fleshier than the Kerry but was thought to look a better milker than the Kerry. Short cows with large udders seem to showcase the udder in a much more extreme way than a longer legged cow though the udder could be of the same size. The article really goes on to highlight the excellent milking attributes of a Dexter to great lengths. A point worth mentioning is that “there is hardly a prettier sight than a herd of Dexters grazing in a park”. I personally can’t help but look out at my hills and know this rings true to me today, just as much as it must have to the writer of this article in the past! Dexters truly are practical and beautiful when bred for all these amazing Historical traits!


Breeders have long been concerned with breeding to “type” and a few points to mention in this last photo that align with the Standard Description of a Dexter is the color being “Whole black or whole red”. The “Head short and broad” with “great width between the eyes”, and “tapering gracefully twords the muzzle. Dexters definetley impress with their specific beautiful traits and charming ways which took hold of many a wealthy land owner who could aford to buy any exotic cattle they chose. In conclusion Dexters and their “pretty little calves are very fascinating”! They are Irish and Proud of it and those of us who breed them, have been taken by their Irish Charms.

Dexters ARE Irish and Proud of It Read More »
Historical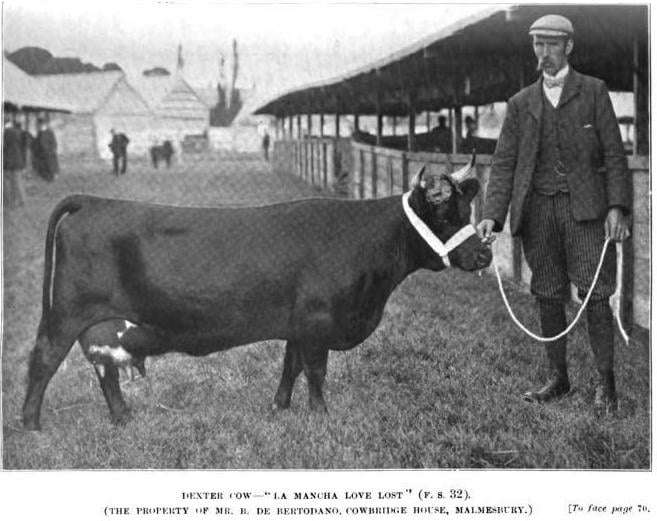
Dexters have long been hailed as hardy and thrifty even adaptable to locations from Africa to snow laden areas. This article I am sharing was written by R. Tait Robertson; he was a famous and most influential Dexter breeder for his day. He was not just any armature Dexter owner, since he was a foundational breeder of Dexter cattle and a generational farmer. He explained that” I have on my farm over 100 of them (Dexters) lying out at present, and they will continue so all winter, getting nothing beyond what they can pick up and a small portion of hay night and morning”. What this means is that Original Dexters could get by on just a little, but of course they could thrive on even more. It was often said that when the Dexters of Ireland went to the manor lands of England they grew greater in size due to the surplus. Dexters can do well on just forage and hay alone with no grain needed. They can excel on the best rations and produce even more, but if times get tough, they can more than get by.

Mr. Roberston was a very influential breeder, breeding in Malahide, County Dublin, Ireland. His family later had Church Farm in Babraham, Cambridge. His Dexters were esteemed as quality and were very sought after by the English who wished to keep them. He is the son of James Robertson. They were not just multigenerational farmers but multi-generational Dexter farmers who helped shape Dexters in their early years by breeding and selection. Dexters as we know them then owed a great degree of tribute to this influential family. Mr. R. Tait Robertson was also a judge for Kerry and Dexter cattle. He judged them by the merit that this article speaks to. Someone may say that Dexters are a beef breed that can milk, but Mr. R Tait Robertson said they have “equal merit” to Kerry cattle. They were not transformed in England to a milking breed but rather selected and bred by breeders like the Robertsons for great dual-purpose traits and were heavy in exceptional dairy traits. When R. Tait Robertson speaks to their equal merit remember that he was a judge for both Kerry and Dexter cattle and those judges gave prizes and entered both Kerry and Dexter cattle into the foundation herd books for the Royal Dublin Society. Dexters are not, nor have they ever been a beef breed that can be milked, but rather a dual-purpose breed with equal merit in milking traits to an ancient breed of dairy cattle (Kerry cattle) that can excel at grass-based feeding.

Mr. R. Tait Robertson was the owner and or collector of the cattle in the La Mancha Herd. He or his family may not have bred them all but rather selected some as foundational cattle for the Dexter breed. You will often see La Mancha Dexters registered to him, his father or Robertsons and sons. His Dexters traveled to many countries and those Dexters that could be found “Lying out all winter long, getting nothing more than what they can pick up and a small portion of hay Night and Morning” run in the veins of our Dexters today. This article I shared was written on 16 December 1899 and La Mancha Love Lost was born in 1897. She was qualified by inspection most likely by Mr. R. Tait Robertson and would have spent time in his field while this article was written. It’s nice to think of such a beautiful cow lying out in your pasture all winter long, getting nothing more than what she can pick up and a small portion of hay night and morning then still looking so beautiful! That’s the kind of Dexter I want.
Dwarfing within the Dexter breed is entirely hereditary and does not occur in an individual as a result of a mutation.
Genetics of the Dexter Breed Read More »
Historical
Dexters have long been promoted the same way time and time again, “Docile and Hardy little cattle, dubbed the smallholder’s cow because of their ability to exist on about half the acreage of other cattle.” This is the niche market of a Dexter. They are well suited to beginners because they can endure a bit of accidental neglect from new owners and be a great fit for people who have small acreage. Today when large acreage is becoming increasingly expensive in many areas, but people are feeling a strong draw to get back to the country, the small acreage Dexter cow is the most perfect sell point. This is a Hallmark of the breed and one that should be promoted.
Dexter cattle are also a good fit for people who need a smaller amount of both meat and milk, but yet they are still “renowned for the quality and quantity of their milk, second only in butterfat content to the famous jersey, and for small lean beef joints of excellent flavor”. There are other breeds than Jersey that outperform Dexters in cream content but usually they are not breeds that produce a good quantity of milk. The Highland for instance produces about 10% butterfat, but for its larger size produces quite a bit less by volume for its size. This is why the Dexter is an all-around great little cow.
The current average amount of people in a US family today is 3.15, so in a small 3-person household butchering a Dexter steer goes a very long way. As Dexter beef producers we will have a much easier time selling whole or halves to people. This avoids having to get a USDA certified meat facility which in some areas could save you more money on butchering costs. Many people are more accustomed to the idea of buying meat in a smaller quantity when they need or want it. With smaller sides you can market to people to be able to only fill a portion of their chest freezer and have space left over for other things. If you have a larger family that enjoys eating lots of beef and drinking more milk, no problem, enjoy the benefit of growing out a larger herd with more Dexters!
This article was written 09 July 1992, and you will see the addition of dun is mentioned to the original color of black and red. Dun was added to the allowable Dexter colors and today many people never knew that black and red are the only 2 original colors.
Written By Danielle of Bryn Mawr
The Dexter: The SmallHolder’s Cow Read More »
HistoricalBy Judy Sponaugle of Legacy
Another registry “innovation” finds the US herd a hodgepodge of mediocre and forgettable initialed herd names. The US is the ONLY country in the world that has so little respect for Dexters they guarantee breeders basic anonymity by using initials of farm names as herd identifiers! Goodness but it IS forgettable.
Here’s an example. I was trying to convince a new breeder about to register a first calf NOT to use the initials encouraged by the US registries for it all but determines anonymity for their herd. Truth be told. . . . there are only two initialed herds in the US I remember by initials, both because the owners were/are prominent in the breed. So, . . . I gave this person examples of wonderful and imaginative herd names, and then I looked at the state of Virginia ( where the owner lived) and picked out three herds with initials. I know most herds and owners by heart through constant research. . . and I looked at the initials and began the process of trying to remember the herds. It was a struggle! One of the herds I knew very well because my own bloodlines founded the herd and it was a perfect example of how even a constant researcher will NOT recognize herd initials. Almost guaranteed anonymity and obscurity unless the person becomes a huge long-term breeder with a large herd.
Woodmagic was chosen by Beryl Rutherford because it was based on a favorite book from childhood, and all her Dexters were named after woodland creatures and birds. Grinstead brings a smile to one’s face, with or without the beautiful photos of that herd and it’s dominance in pedigrees through the years. Most English herds were named after the homes or estates or towns where they grazed. It would be interesting to know the history of the choice of La Mancha for the Robertson family’s Dexter herd, but Round Chimneys leaves little to the imagination. Parndon was a parish in Essex, England, and the origins of Ypsitty is still a mystery to me. My least favorite herd name in the English records is Bryn-y-pin because it was difficult to type.
American herd names prior to the 90’s were also imaginative and memorable. Peerless certainly lived up to it’s identity, and every Missouri Dexter owner would immediately know the roots of “Shome”! Shamrock immediately brings to mind the hallowed green leaf of Ireland, while Rainbow and Rainbow Hills are colorfully soothing to imagine. Talisman is a herd name I always liked, and there is a Virginia herd that lives in literal “Paradise”. The Lone Star and Cascade herds identify their geographic locations but also denote history, and Chautauqua identifies an area of NY where the herd is located. ( Another typing challenge for me).
Then we have SGF and SMD. These herds are owned by long-time well known breeders. Can you immediately identify these herds or do you have to stop and think as I did with a herd I knew as well as my own? In England, or Australia, or even Canada, you would most likely know these herds as Spruce Grove or Silver Maple and the identifier would be far more memorable.
One registry started this and the other continued this nonsense of encouraging owners to use initials and give US Dexter herds guaranteed mundane, boring, and unimaginative herd identifiers. This is an “only in America” tradition that needs to fade into the obscurity IT deserves. Please registrars. . . . STOP . .. . .suggesting to owners to use initials. If you are fairly new to the breed. . . . . then CHANGE those initials to a memorable herd identifier and INSIST on it.
IF. . . you are a new breeder and happen to read this page. . . . . . . . . . . . . your Dexter breeding program deserves a unique identity. I strongly urge you not to be led down the initialed path to anonymity.
THINGS TO CONSIDER ABOUT YOUR HERD IDENTIFIER. A LITTLE BIT OF HISTORY! Read More »
HistoricalMany thanks to Judy Sponaugle of the Legacy Registry for providing the Irish Dexter Cattlemen with this valuable information. This is the first in a series of excerpts from The American Kerry and Dexter Cattle Club.
It is a great find for all you Dexter history buffs! Seeing some of the old advertisements and recognizing some of those herds was a thrill for me.






The American Kerry and Dexter Cattle Club ….series 1st Installment Read More »
HistoricalHere is the second installment in the series of The American Kerry and Dexter Cattle Club brought to us by Judy Sponaugle of Legacy. Hope your enjoying the series!






The American Kerry and Dexter Cattle Club….series 2 Installment Read More »
HistoricalHow much dairy should we put in to a Dual purpose Dexter cow. If you were to consult the English herd books they would say 40 percent for the “Bag” with the remaining percents being 15 for the “Head and neck”, 25 for the “Body, top line, under-line, ribs, setting of the tail, shortness of the leg, ect.”, 10 for “Quality and Touch” and 10 for “Colour”. So 40 points goes to the quality of the udder while 25 points gets divided up between the “Body, top line, under-line, ribs, setting of the tail, shortness of the leg, ect.”. It seems to me that in Dexters the focus today tends to fall primarily on mostly two aspects alone: shortness of leg and body type with general conformation coming in at the end. Even with 3 aspects it only accounts for 25 points for a Dexter. So there is a hyper focus on 25 % of a Dexter while the 40 percent in often neglected. The length of a cow’s leg and it’s depth are not the only traits that define a Dexter. Of course, we can’t forget the other traits that almost no one talks about, the “Head and neck”. You don’t get much meat off a head but it adds a distinct breed defining trait to a cattle type to set them apart.
It’s interesting to note that Kerry cattle that became a distinct dairy breed separated from the dual-purpose Dexter also list 40 points for the udder. The only difference is that more details are mentioned about the bag, “Udder, size, situation of teats, milk veins and escutcheon”.
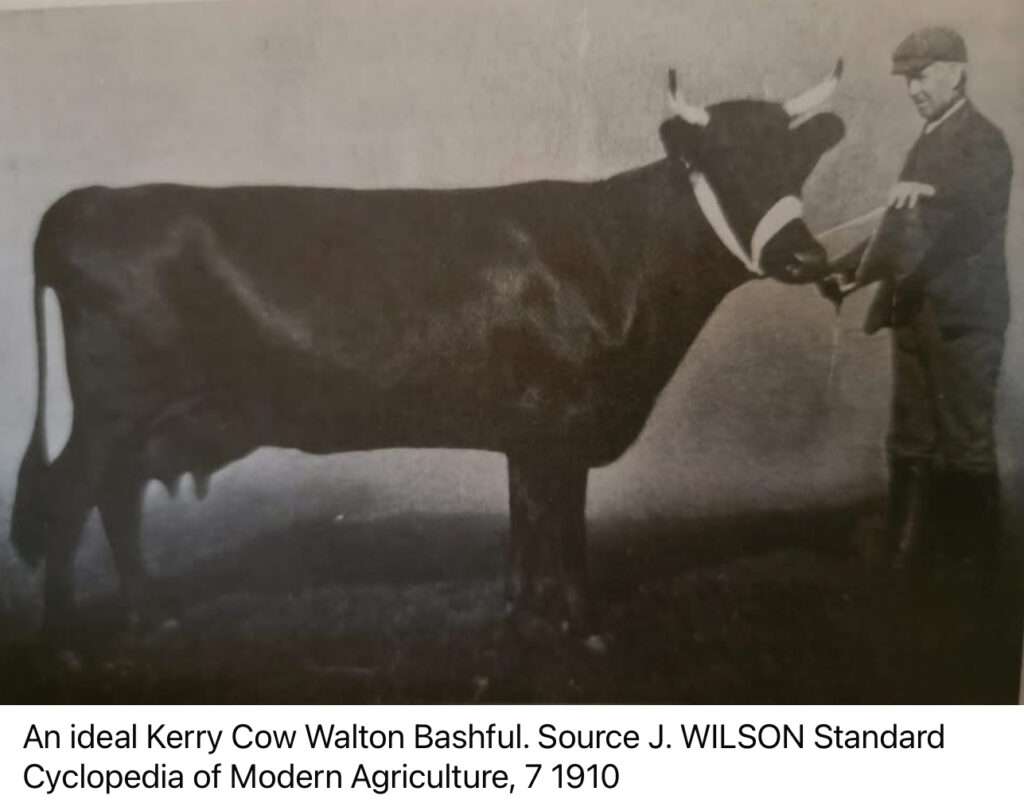
Now before major concern sets in, consider that this point system is based on an ideal cow. There will always be cows in a breed that are not ideal, but the goal is to breed for the ideal cow. If you look at the 3 pictures of Kerry cattle, I will share you will see that Walton Bashful is listed as ideal and her udder is the best of the three cows shown. I’d say if an udder is ideal enough for a Kerry it can likewise be good enough for a Dexter that uses the same 40 percent system. Of course, there is no problem with having an even better udder than this cow does! The next Kerry is Valencia Eileen III. You will immediately see that she could improve on her forward attachment, but she was a Kerry all the same. The final cow is Ard Caeina Una. You will see she has some attachment issues, and you will tell that her udder is hanging lower by her hocks. The placement of her teats are too close and awkward but they were still put to use, as you will see by reading her milk record. Her yield 14,562 lbs with her butterfat at 4.33 percent. Still a valuable Kerry cow. With Dexters we need to seek generational improvement in dairy traits as Dexter’s udder points are just important as Kerry cattle, but we also need to remember that improvement is generational and culling cows with good production and butterfat won’t instantly fix a problem. It could lead us to a breed full of cows with very tight nonproductive udders just because new people think a tight looking udder is an aesthetically pleasing udder.


The Dual Purpose Dexter And The Kerry History Read More »
HistoricalLegacy Dexter Cattle Registry seeks to preserve Irish Dexter bloodlines from the English upgrade/appendix registry. Support Legacy Irish Dexters by registering your Irish Dexters.
The Gift From Our Ancestor Read More »
HistoricalWhen you consider that people in the past were a bit confused about the difference between a Dexter (Dexter Kerry) and a Kerry you understand why it confuses people now. The fact that Dexters were called Dexter Kerry for many years after the two breeds were split from each other, continued to confuse people, thinking that Dexters were still no different than the Kerry breed. It’s interesting to note that in the Royal Dublin Society Kerry cattle were described as shorter than other cattle, so short that a full-grown cow was said to be the size of just a yearling (that was in 1890 when most breeds of cattle were smaller than they are now). As you can see Dexter cattle were not the only short ones as Kerry cattle have a long history of being smaller in stature too. If you have Dexters you can recognize that there is a strong similarity in the description of size among many of them. I have people come to my farm and confuse a full grown dehorned cow for a yearling of another breed. Once the two breeds were separated there immediately would have been a breeding divergence. Very detailed breed standards were already created that defined Dexters before 1911 at the time of the first printing of The American Kerry and Cattle Club Bulletin one. Following those standards for all the years prior would have helped pave the way for the breeds to be separated and defined as their own, but yet the confusion remained as can be seen in the below picture, because the breeds had so many similarities.

The cow in this photo above is from Bulletin One of The American Kerry and Dexter Cattle Club. It was printed in October 1911. This is the old name for the ADCA (American Dexter Cattle Association). The cow photographed is named Waterville Violet and in her description the title Dexter has been crossed out. Was this just a scribble that someone made at a later date randomly or was it something scratched out to add a correction after it was printed?
If you check the records in the ADCA you will find no Waterville Violet mentioned. If you look for a Kerry cow by the name of Waterville Violet you will turn up multiple citations of her as a Kerry cow. It looks like Violet was a Kerry heifer who calved in 1902 so we can get an idea that she was already quite mature by the time she was mentioned in the 1911 Bulletin. As much as things can be confusing it’s fair to say Dexter or not there are still purebred registered Dexters of today that look like Violet.

James E. Butler owned the Waterville herd. Mr. Butler owned and bred both Kerry Cattle and Dexters, as many of the original breeders of Dexters did because in selection the black more dairy type became Kerry and the cattle a bit thicker, black and red, possessing dual purpose traits became Dexters. Butler was also one of the judges at shows for evaluating Dexters for the entry into the herdbooks. He had a long history in the area. James Butler would have been an excellent choice for a judge due to his first-hand knowledge of Kerry and the native cattle of the land. Waterville is known as Coirean in Gaelic or “Little Cauldron”. It is a village in Kerry. The ring of Kerry passes through this town. It’s good to know that Dexters and Kerry cattle were being selected and registered by men with first-hand knowledge like James E. Butler of Waterville. I would suppose they were far more confident in the difference between a Dexter and Kerry when they were making their evaluations. I hope this has shed a little more light into the past of Dexter and even Kerry cattle.
For Many the Dexter breed may have a confusing Past. Read More »
HistoricalCalling all Beef Breeders!!! For anyone who likes a bit of Beef in their dual-purpose Dexters here’s something for you! Have you ever wondered what the Live weight, the Average daily weight gain of live weight, Weight of dressed Carcass, Percentage of carcass to gross live weight, Weight of loose fat and Weight of hide was on a Dexter Kerry or a Kerry and a Dexter Kerry cross was at the formation of the Royal Dublin Society in 1890? I wish all fields were complete as some are missing but it’s a good start. Well, here are some answers for you, so let’s see how these weights compare today. Comments are welcomed. By the way Tommy Titmouse was an Angus Dexter Kerry cross.
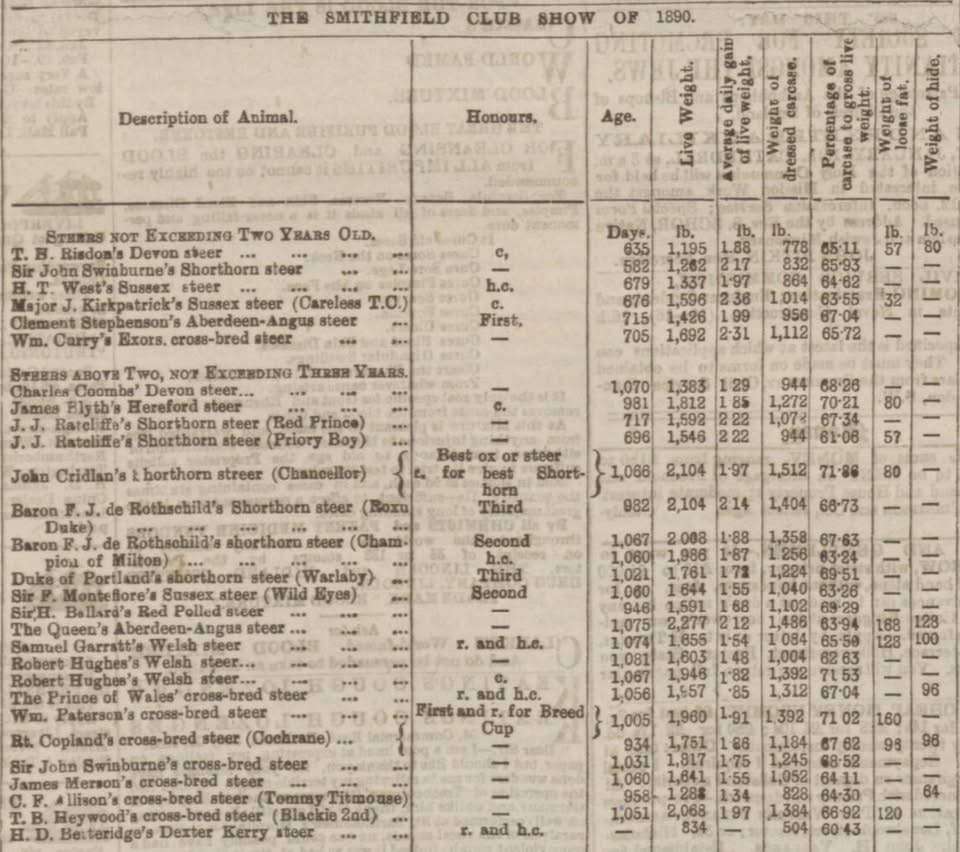
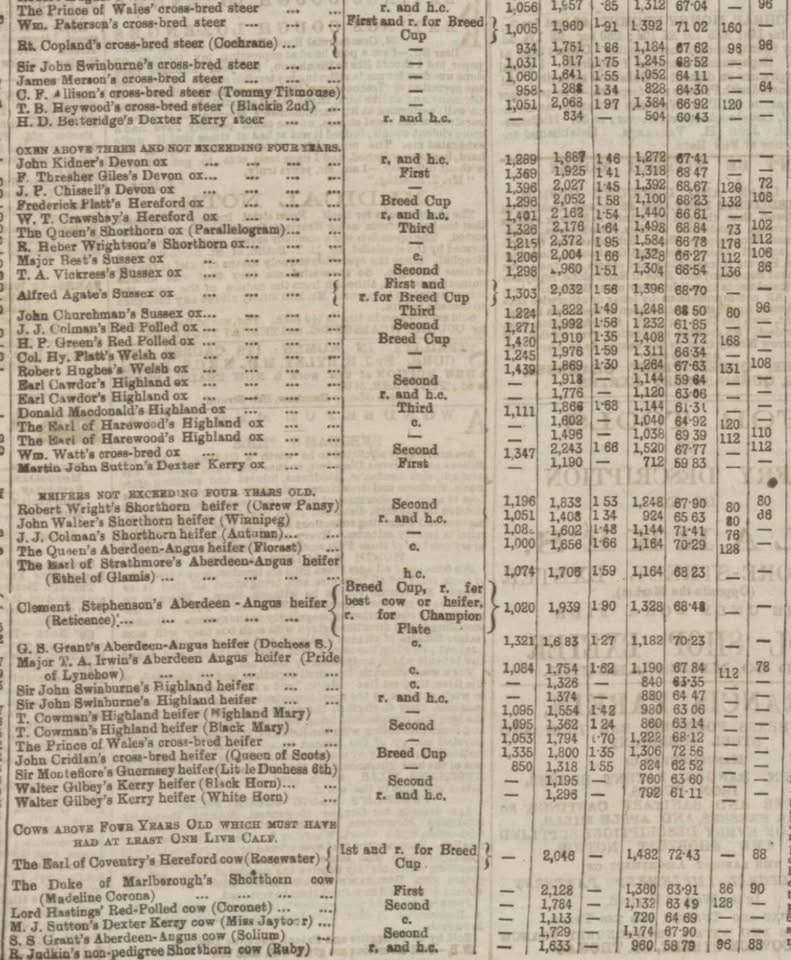
LET’S TALK DEXTER WEIGHTS! Read More »
HistoricalThis article written in Gloucestershire on 27th March 1986 represents a long memorable chapter of the pages in History of Dexter cattle. The Dexter in this article is being noted as truly dual purposed, possessing fine quality small joints of beef, all the while being able to suckle two calves at once and raise 8 commercial calves in one year. This all seems an even more amazing feat when you consider one of the cows being spoke of was 34 inches. Thirty-four inches, how many Dexters today meet these amazing statistics? This article when I compared to other historical information sites a higher average milk production than some historical amounts in Dexters that I have seen at 4.5 gallons per day. This figure is not rare by any means but not necessarily a given rate with some Dexters producing a bit less.
Dexters are being stated as being small and valuable for grazing under plum trees so as not to damage the trees. At the time of this article, Dexters are listed on the Rare Breed Survival Trust, but are no longer being listed as endangered as they once were prior to the articles printing. When we consider today with so many pedigree Dexters in great numbers it is hard for many to believe that Dexetrs were once so rare. But yet how many rare Jems are left like the Dexters being mentioned from these days, just back in 1986? Perhaps the Dexter of 1986 is rarer than we think.

SMALL CATTLE CARRY AWAY BIG HONORS Read More »
HistoricalDid you know the look of a Dexter’s head was important to breeders and that there was what was considered a “Dexter Head”?
“Harley Penelope is good to carry in one’s eye as a type of a good Dexter cow. She has the quality and character, a sweet small Dexter head and carries her horns well.”
“I lost my heart to Red Rose, a very beautiful cow, she has the Dexter head to perfection”
Did you know that Dexters were known to give a good milk yield for their size and excelled on lower quality pasture?
“Naturally in these times, when the economy of feeding stock is of importance, the hardiness of a Dexter, the large milk given by them on a small quantity of food, and their ability to thrive on poor pastures make them particularly attractive”
Did you know that breeders put a lot of emphasis of breeding to “pedigree and type” not just pedigree or type alone? That people wanted to keep their diets similar so that they could retain their original attributes including size and hardiness.
“It must be born in mind that these cows are not fed on cake: no doubt on higher feeding these records should be raised to 1500lb or 2,000 lb more than those given above, but Lady Kathleen Morant told me: I do not feed with cake ect., I try to keep them as much as possible on the same lines as the Irish peasant would do because I feel that is the best way of keeping them true to type and from getting them large and coarse.”
All these thoughts can be found in this newspaper clipping from 1917, in reference to Kathleen Morant’s Dexter herd along with pictures that describe even more than the words written in black and white can relate.






The importance of the Dexter Head Read More »
HistoricalEnjoy this video from 1949 to see what a common herd of Dexters may have looked like at that time. It would be interesting to see what observations new people to the breed would take away from the video if they were to compare them to many Dexters now available for purchase.
Understanding where Your Dexters came from will Give you a vision for their future. Read More »
HistoricalWhen people ask me why I think the history of Dexter Cattle is important this is just one great reason that I may give. If you see changes over years happening during the foundational years you can see how breeders were interpreting improvement during a time when people were focusing on breed selection to adhere to a standard that was the norm for the day. You can also see changes that happened over the years and genetics that were diminished in frequency or increased in frequency.
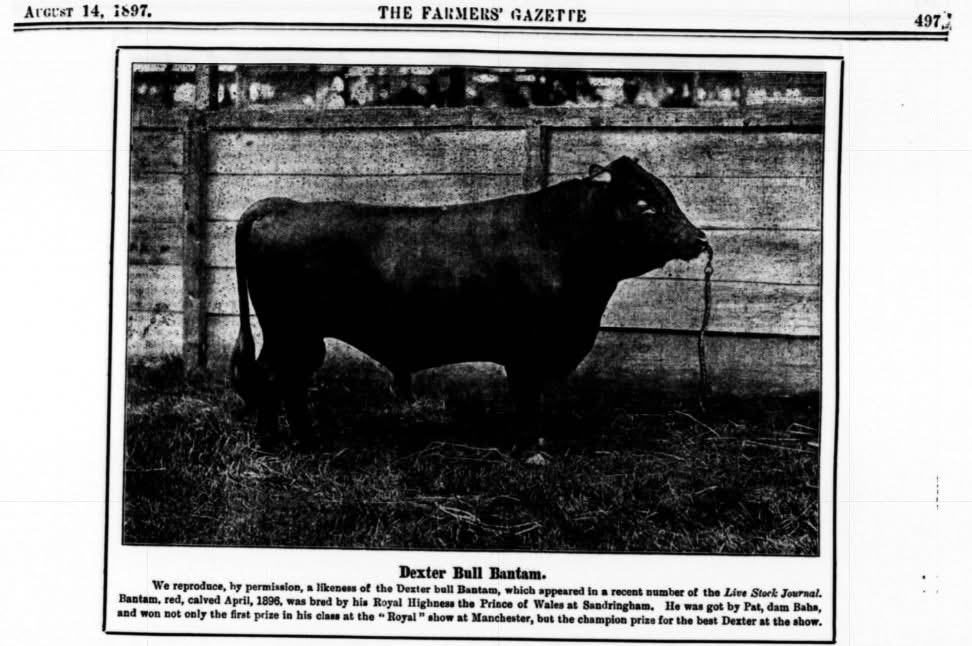
Dexter cattle, though many were black in the early days compared to today this bull Bantam in the top photo was red. During the foundational years it was much more common to find a red Dexter than it was in America prior to people intentionally selecting to increase or preserve red Dexters. Now today red is so common that if someone did not know the History of the breed, they may think it was the predominate color from the beginning.
It’s an interesting point to note; this bull Bantam was bred by the Prince of Wales at Sandringham in 1896. Bantam is what a Champion prize Dexter looked like in 1897. This location is situated in Sandringham, Norfolk, England. Dexters had a very early start of popularity in England being bred by some very noteworthy people. In 1862 Sandringham Estate was under 8,000 acres were as today the acreage is closer to 20,000 acres. If you look at the second picture you will see that in 1914 Dexters were still being breed at Sandringham by the King. The first bull Bantam has a good broad form for a Dexter of his day but when you compare him to the form of the Dexter bull that the King had in the photograph in 1914 you will see he has a broad back end as well as his front. It would be really nice to see a clearer photo of the second bull but we can see enough to consider some of his conformation. Improvements with each generation are very important and should always be improved based upon the breed standard of a breed, because without a standard there is no direction for improvement. While improving on beef traits one must always remember to improve dairy traits equally too, so as not to diminish dairy traits in favor of beef. A beautiful beefy bull is of little value to a dual-purpose breed if he only throws daughters that lack quality dairy traits. When both traits are in harmony you get a great dual-purpose Dexter.

History helps track changes in a herd over a period of years. Read More »
HistoricalPoor Man’s Cow to Luxury Cow
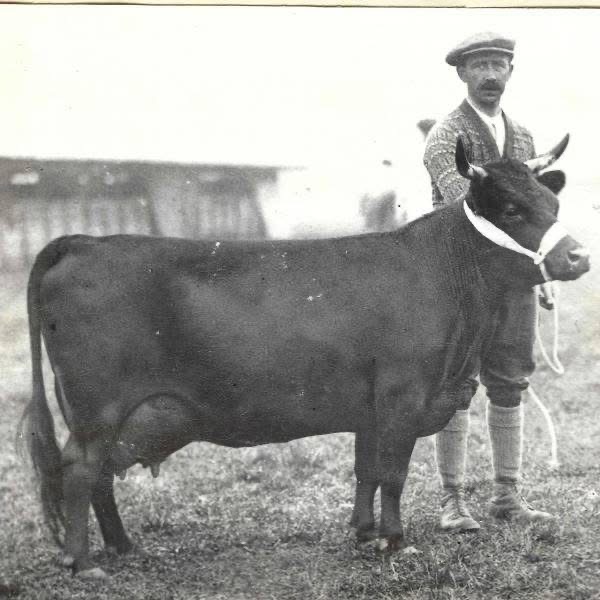
How did the Poor Man’s Cow become owned by the wealthy and famous. Dexters and Kerry Cattle became recognized for their unique hardy attributes, Kerry for milk and Dexter for milk and meat. Dexters were known to get by on less, produce rich milk and raise a healthy vigorous calf for their owner’s table. Dexters were bred to their breed specific traits transforming them from just any poor Irish cows to these 2 beautiful, registered Dexter cows we see in these two later photos.
They were rare and they were at risk of being cross bred out of existence, but breeders in Ireland started selecting and registering Dexter cattle with breed defining traits to preserve and register them in a herd book. Once the promotion of Dexters began every wealthy aristocrat wanted one. All of a sudden, they were not the Poor Man’s cow but rather for a short spell until the numbers grew, cattle that only the wealthy could afford. Consider as this article states a $200 dollar Dexter cow from 1915. This is the equivalent of $6221.78. I checked multiple inflation calculators to verify that number as being correct. With the highest price the ad mentions at $350 in 1915, you would pay $10,936.81 today! Consider today we pay less for quality breeding stock. Rarity always drives the price up and just like with the rarity of gold it dictates the price.
Registered cows were important then and today. Registered Dexters will always hold a higher value than unregistered. Still with Dexters it took devoted breeders to breed Dexters according to the Dexter Standard to the highest quality like the 2 cows you see in the photographs. Not every Dexter cow was nearly as ideal as these two beauties. Compton Daphne, I speculate is a Chondro Carrier while Grinstead Watercress I speculate to be a non-carrier. Of course, we can never go back and test them so it’s just speculation. Both are extremely well bred and both fit the standard well.
So, as you can see Dexters are a dual-purpose breed that can be bred by multiple types of people regardless of fortune because they are a great pick for everyone. Whether you’re a small homesteader trying to save money with a thrifty headache free cow or someone who just wants to raise them as beautiful lawn mowers true Dexters are a great fit for these reasons and so many more!
30 Jan 1915 is the date of article written.
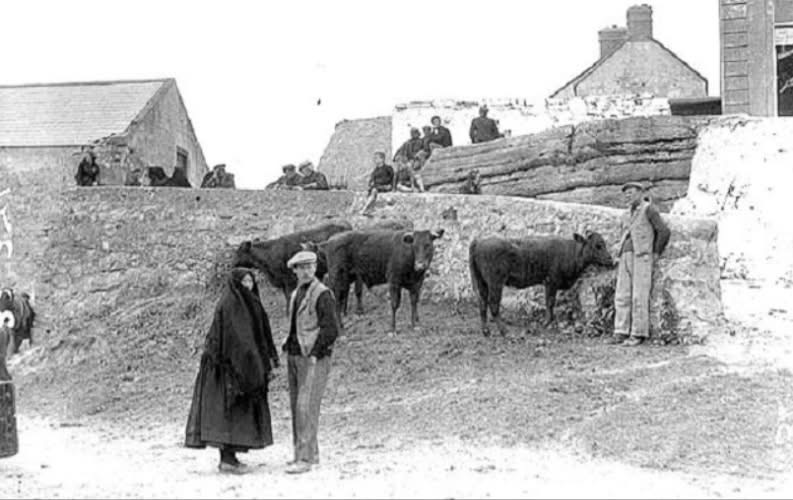
Photo of cattle in town are common type of Celtic cow that roamed Ireland.
Other two photos are of registered Dexters.




Dexters – Poor Man’s Cow to Luxury Cow By Danielle Lowther Read More »
Historical